
The Section 179 election amount is calculated in Part I and bonus depreciation is calculated in Part II. You must add this form to your other business tax forms or schedules when preparing your business taxes. The purpose of depreciation and amortization is to spread the cost of an asset over its useful life. Both are recorded on the income statement and later become tax deductions.
Financial
The way cost is allocated when using these two concepts can also vary. Amortization almost always follows a straight-line approach, meaning the cost is evenly spread across the asset’s useful life. Looking for a comprehensive fixed asset and depreciation accounting software? Thomson Reuters Fixed Assets CS has the tools to help firms meet all of a client’s asset management needs. The same concept applies for depreciation expense, which is a portion of a fixed asset that has been considered consumed in the current period and is then charged as a non-cash expense. Percentage depletion and cost depletion are the two basic forms of depletion allowance.
- You can’t depreciate land or equipment used to build capital improvements.
- This brings your net profit down to $95,000, which is not that significant of a difference.
- If the asset is a vehicle, the depreciation value is calculated at an accelerated speed at the beginning of the period as it loses most of its value in the first few years.
- And when it comes to intangible assets, amortization helps you recognize the declining value of these assets as they contribute to your business operations.
- Assets deteriorate in value over time and this is reflected in the balance sheet.
- Your choice should align with how the asset is used in your business to provide the most accurate financial picture.
- Amortization can provide tax benefits for businesses by allowing them to write off expenses over time.
Depreciation or Amortization Schedule
- The declining balance method calculates depreciation faster than the straight-line method, meaning that a higher percentage of the asset’s value is depreciated in the early years of its useful life.
- Properly applying these concepts can enhance overall financial health.
- If a borrower refinances the loan, makes extra payments, or misses payments, the original amortization schedule is modified.
- Accurate record-keeping ensures compliance with tax laws and accounting standards, and it also provides the data you need to make informed financial and managerial decisions.
- Work faster, manage better, and stay on top of your business with TallyPrime, your complete business management solution.
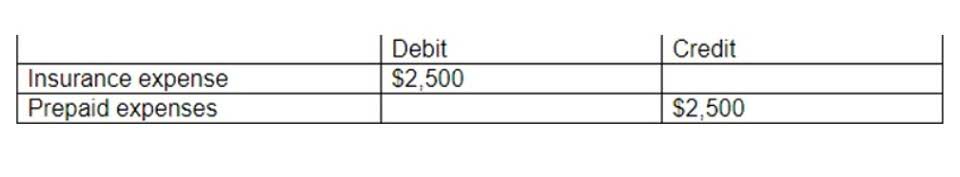
The process of spreading the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life. A home business can deduct depreciation expenses for the part of the home used regularly and exclusively for business purposes. When you calculate your home business deduction, you can include depreciation if you use the actual expense method of calculating the tax deduction, but not if you use the simplified method. The IRS requires businesses to follow specific regulations in order to be able to deduct the costs of business assets (the IRS calls them “property”). The main differences are in the types of assets they account for, as depreciation covers physical assets while amortization covers non-physical assets. Depreciation and amortization are accounting methods used to allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life.
Using the Accumulated Depreciation Method

This amortization vs depreciation provides a more accurate picture of your business’s true performance. Depletion is another way the cost of business assets can be established. It refers to the allocation of the cost of natural resources over time. For example, an oil well has a finite life before all of the oil is pumped out.

Tax Saving Strategies for LLCs, S-Corps, and C-Corps
Each year the asset is used, its value is paid back by the same amount. By the end of the assigned “object’s” useful life, its book value is 0. For example, machinery might break down over time, so its value goes down. Knowing how to apply them affects everything from daily bookkeeping to annual tax filings. Over the next five years, you will write off $3,000 each year to cover the cost of this patent. Sigma is a the leading business broker with offices in Dallas/Fort Worth Texas with roots from 1984.
Conversely, depreciation is similar to amortization but applies to tangible assets like buildings or equipment. It’s spreading out the cost of these assets over their useful lives. Amortization and depreciation are used to spread the cost of a tangible or intangible asset over its useful life. Amortization applies explicitly to intangible assets such as patents and copyrights, while depreciation applies to tangible assets like buildings what are retained earnings and equipment.
Understanding the proportional amortization method

Gain hands-on experience with Excel-based financial modeling, real-world case studies, and downloadable templates. Upon completion, earn a recognized certificate to enhance your career prospects in finance and investment. Both depreciation and amortization deductions are reported on IRS Form 4562 filed with the annual tax return. It’s also important to note that the IRS specifies which assets are depreciable or amortizable, their useful lives, and approved methods for deduction Bookkeeping vs. Accounting calculations. Understanding these underlying differences is more than just academic; it directly influences how you record and report expenses and assets in your financial statements. These conceptual variances are foundational to both managing your business’s resources effectively and maintaining regulatory compliance.
- The two non-cash expenses are recorded at the top of the cash flow statement (CFS) as an add-back to the accrual-based net income.
- Choosing between depreciation and amortization doesn’t have to be complicated.
- This includes how much you use it and what it will be worth in the end, called its salvage value.
- The standard accounting practice for most companies—exceptions aside, such as capital intensive companies—is to consolidate depreciation and amortization on the cash flow statement (CFS).
- Accounting guidance determines whether it’s correct to amortize or depreciate.
Tax vs. book depreciation and amortization
Now, that can sound good, but let me tell you, back in 2003, it was not easy to sell a business. It’s important to note that the decision to amortize or depreciate an asset is not always straightforward, and it may be necessary to seek the advice of a financial professional. To aid your understanding of both methods, here are their similarities. Unlike depreciation, there’s no salvage value to consider since you can’t sell or reuse a patent after it expires.
Declining balance depreciation is used when the company wants to expense a greater portion of an asset early in its life and a lesser amount later in its life. Of these six methods, only straight-line amortization is commonly used. We’ve covered a lot of ground, but as we move on (and begin to wrap up), we touch on the different methods of amortization and depreciation below. But, in 2023, your company gets featured on a small business podcast. Demand goes through the roof, the machine is put to the test, and it produces a whopping 15,000 mugs. Now your depreciation expense is $15,000 as opposed to the $5,000 that would have been booked using straight-line depreciation.
